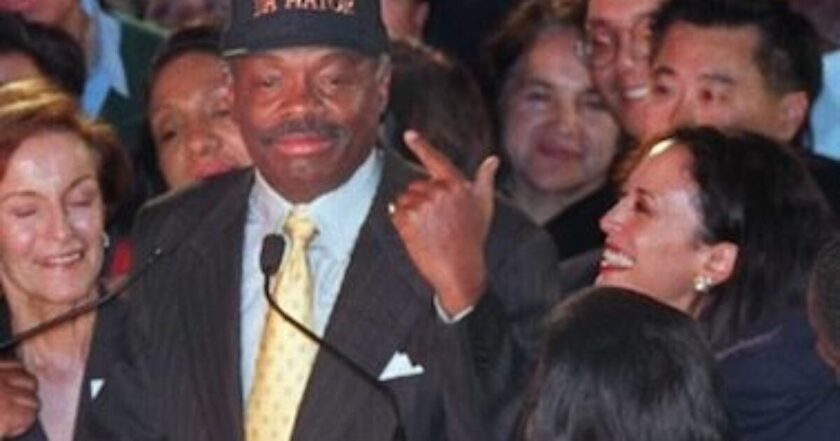

In today's political climate, where every aspect of a public figure's past is scrutinized, it's entirely appropriate to examine Kamala Harris' relationship with former California State Assembly Speaker Willie Brown. Harris' political ascent, tied to her personal relationship with the powerful politician, raises legitimate questions about her rise in San Francisco politics and the path that eventually led her to the vice presidency.
Kamala Harris was 29 when she began a relationship with Brown, who was 60 at the time. Brown, often referred to as "The Godfather" of San Francisco politics, wielded enormous power and influence. Their relationship was far from a simple personal affair; it coincided with significant advancements in Harris’ political career, many of which can be traced directly to Brown’s backing.
How Brown Elevated Harris' Career
Willie Brown's support for Harris wasn't subtle. He appointed her to two lucrative state commission positions during the 1990s, one of which was the California Medical Assistance Commission, where she earned over $70,000 a year, equivalent to $120,000 today. Harris held that role from 1994 to 1998, attending only two meetings per month. Critics in the Democratic Party expressed frustration, not only because Harris lacked the necessary qualifications for the role, but because such positions were typically reserved for seasoned political allies who had helped keep Brown in power. Instead, he gave it to Harris, who was his girlfriend at the time.

Willie Brown, Kamala Harris' much older lover, not only gifted her a BMW but also helped her secure a second state commission position, significantly boosting her salary and establishing her both financially and politically. This infusion of wealth and political influence laid the groundwork for Harris to advance in her career, positioning her for greater success as she climbed the ranks within California's Democratic Party.
Breaking Up, But Not Letting Go
While their romantic relationship ended shortly after Brown was elected mayor of San Francisco in 1995, his influence on Harris’ political life did not. Even after their breakup, Brown played a significant behind-the-scenes role in Harris' campaign for San Francisco District Attorney in 2003. Brown is known to have used his connections and political clout to steer wealthy donors toward Harris, helping her secure the financial backing needed to launch her successful bid for the DA's office.

Harris, however, publicly distanced herself from Brown as she pursued her own political ambitions. In a now-famous interview with San Francisco Magazine, Harris stated that Willie Brown’s career was "over" and made it clear that it was now her time to shine. This cold dismissal of the man who had greatly advanced her political career is emblematic of Harris’ strategy to shed associations with political figures that could hinder her climb.
A Tough Prosecutor? Not So Fast
Throughout her career, Harris has portrayed herself as a tough prosecutor who fought against predators, fraudsters, and others who broke the law. However, her tenure as San Francisco District Attorney and later as California Attorney General is marked by controversy. Critics argue that Harris was more interested in advancing her political career than serving justice. Reports from both left-leaning and mainstream media have highlighted instances where she failed to properly prepare for her roles, such as not reading critical briefing materials.
Harris’ reputation as a prosecutor also included mixed signals, as she advocated for policies that were tough on crime in some cases but lenient on certain offenders in others. As vice president, this inconsistency has been mirrored by her struggles to find footing in national politics.
The 1995 ABC News Segment: A Viral Moment Revived Ahead of the Debate
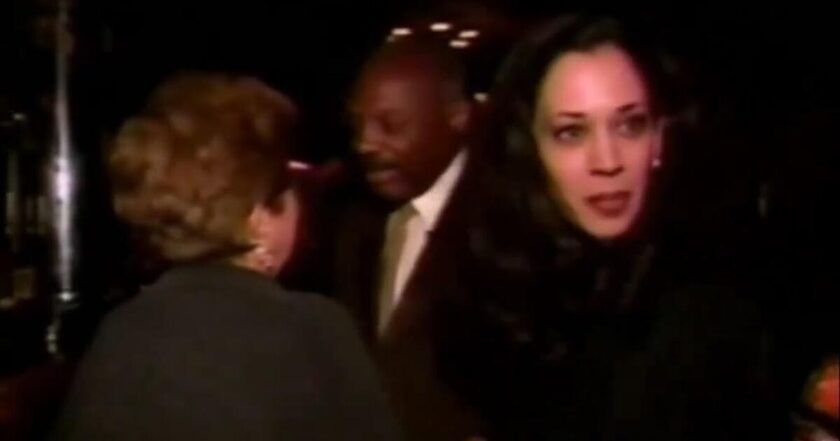

In a notable 1995 ABC News segment, a reporter questioned Willie Brown about his relationship with Kamala Harris during his time as California State Assembly Speaker. The reporter, noticing Harris frequently by Brown's side at political events, bluntly asked if she was his daughter. Brown chuckled and clarified that Harris was not his daughter but acknowledged their relationship. This public moment highlighted the noticeable age gap between the two and underscored the influence Brown had in promoting Harris within California’s political scene, which raised eyebrows even at the time. Interestingly, this clip has recently resurfaced and is going viral ahead of tonight’s debate, reigniting conversations about the early days of Harris’ political career and the role Brown played in her rise to power.
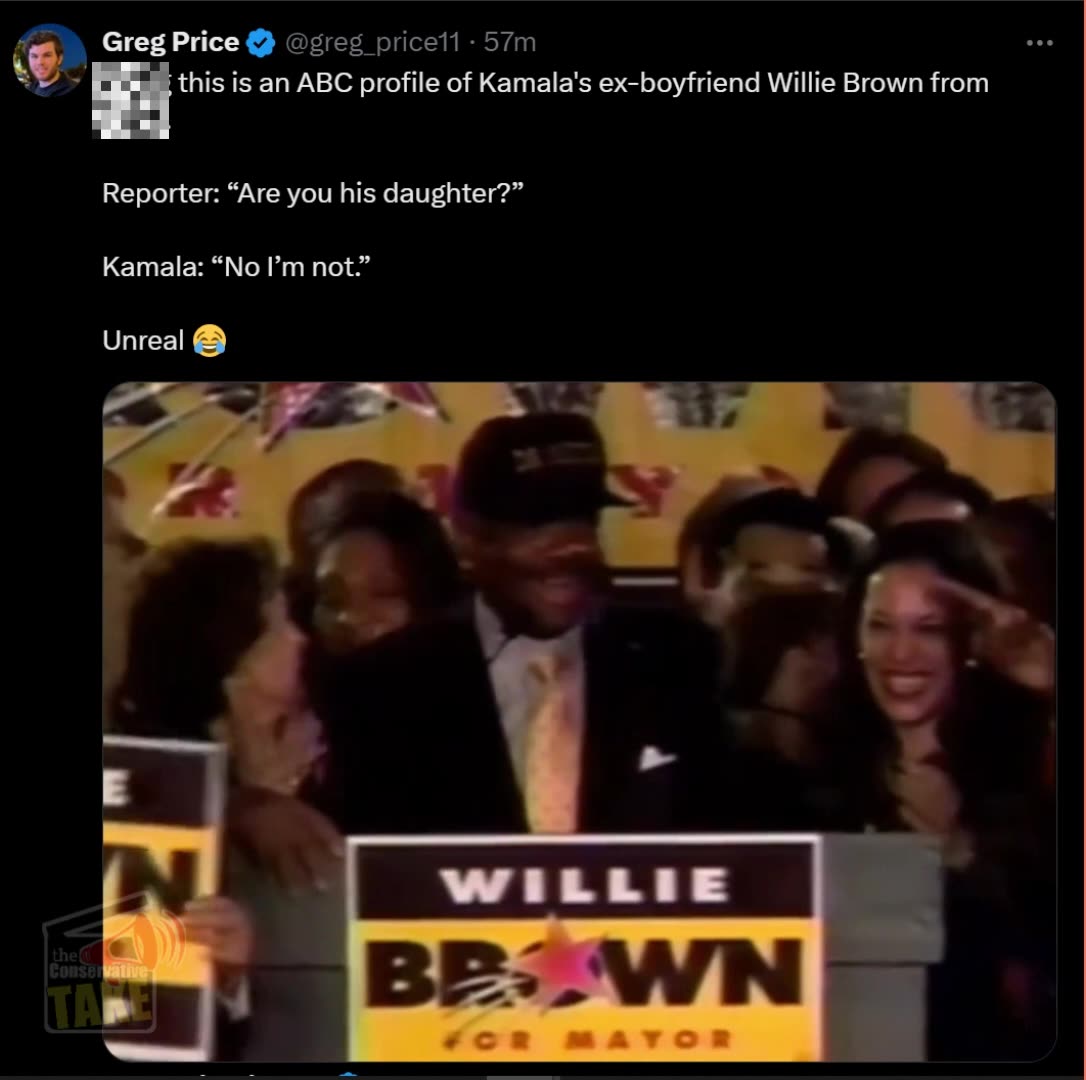
The Willie Brown Connection: Still Relevant
When discussing Harris’ political career, the influence of Willie Brown remains a crucial component. Despite attempts to distance herself from him, the facts of how she got her start cannot be ignored. Their relationship opened doors for her and propelled her into the upper echelons of California’s political scene. The notion that this should not be discussed, or that it is irrelevant to her current position, is misguided. When any political figure's rise to power involves close relationships with influential individuals, it’s natural—and fair—to question the dynamics at play.
In the context of Kamala Harris’ political ascent, her relationship with Willie Brown isn’t just a personal affair from the past; it’s part of the narrative that shaped her career. It’s worth noting that Harris has had to compete mostly within the liberal strongholds of California, where her competition largely consisted of other Democrats. She has never had to face the kind of fierce political opposition that figures like Donald Trump have thrived on, particularly in high-stakes national contests.
As we look to future elections, Harris’ past, including her relationship with Willie Brown, will continue to be a relevant discussion point for those assessing her qualifications and ability to lead. If anything, it raises essential questions about the nature of political power, influence, and personal ambition in American politics. Kamala Harris’ journey shows how powerful connections and strategic relationships can be just as influential as policy stances and public service records. It’s not shaming to ask these questions—it's simply holding leaders accountable for the entirety of their public life.
And in Kamala Harris' case, that public life cannot be fully understood without examining how she got her start with the help of Willie Brown.
Source: Megyn Kelly and Charlie Spiering Podcast Discussion
This information is sourced from a discussion between Megyn Kelly and Charlie Spiering, author of Amateur Hour, on Kelly's podcast from July 23, 2024. In their conversation, they explored Kamala Harris' early political career and the pivotal role Willie Brown, California’s most powerful politician at the time, played in advancing her. Kelly and Spiering highlighted how Harris' relationship with Brown led to key political appointments and lucrative opportunities that significantly shaped her rise within the Democratic Party.












